 Acupuncture
and Moxibustion are an ancient form of Chinese Medicine that has been in use
for the last 3000 years. Because of their many indications, minimize side effects,
low cost and rapid therapeutic effect, these ancient healing arts have remained
popular for ages. Recent research has not only confirmed their effectiveness,
but has also provided modern scientific explanations for why they work. The
theoretical basis of acupuncture and moxibustion is the theory of the meridians.
According to this theory, there is a system of meridians (also called channels)
in the body through which qi (vital energy) and blood circulate, and by which
internal organs are coordinated and connected with superficial organs and tissues,
creating an integral whole.
Acupuncture
and Moxibustion are an ancient form of Chinese Medicine that has been in use
for the last 3000 years. Because of their many indications, minimize side effects,
low cost and rapid therapeutic effect, these ancient healing arts have remained
popular for ages. Recent research has not only confirmed their effectiveness,
but has also provided modern scientific explanations for why they work. The
theoretical basis of acupuncture and moxibustion is the theory of the meridians.
According to this theory, there is a system of meridians (also called channels)
in the body through which qi (vital energy) and blood circulate, and by which
internal organs are coordinated and connected with superficial organs and tissues,
creating an integral whole.
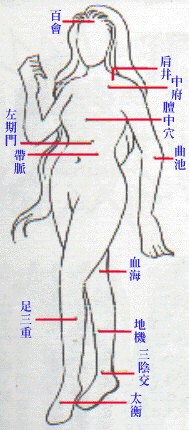
The cardinal conduits of vital energy and blood are called meridians, and the
branches of the meridians, collaterals. Meridians are divided into regular meridians
and extra meridians. The 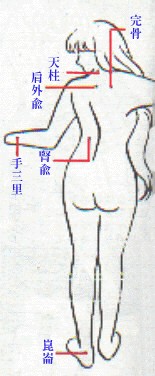 12
pairs of regular meridians constitute most of the meridian system. There are
eight extra meridians. The 12 regular meridians plus the two extra meridians,
one running along the midline of the abdomen and chest, and the other along
the midline of the back, are the l4 meridians.
12
pairs of regular meridians constitute most of the meridian system. There are
eight extra meridians. The 12 regular meridians plus the two extra meridians,
one running along the midline of the abdomen and chest, and the other along
the midline of the back, are the l4 meridians.
Three hundred and sixty-one acupuncture points have been identified along the l4 meridians. The standard nomenclature of these points consists of the Chinese phonetic (pinyin) name followed by the alphanumeric code in parenthesis. Apart from these, there are a number of acupuncture points with specific therapeutic properties not on the 14 meridians; they are called extraordinary points. Each acupuncture point has its own therapeutic action. In ordinary clinics, acupuncture is performed with thin needles.The needles may be of gold, silver or alloy. The needles in most common use today are made of high quality stainless steel. The needle is selected according to the depth of insertion required. For instance, needling a point on the buttock usually requires a long thick needle, while a point on the scalp will require a short thin needle.
The size and length of the needles most commonly used are as follows:
INCH |
MM |
GAUGE |
DIAMETER MM. |
0.5 |
12.7 |
26 |
0.46 |
1.0 |
25.4 |
28 |
0.38 |
1.5 |
38.1 |
30 |
0.32 |
2.0 |
50.8 |
32 |
0.26 |
2.5 |
63.5 |
¡Ð |
¡Ð |
3 |
76.2 |
¡Ð |
¡Ð |
4 |
101.6 |
¡Ð |
¡Ð |
5 |
127 |
¡Ð |
¡Ð |
A good needle is one that is strong and flexible and has a round, smooth body
and tip shaped like a pine-needle.
Moxibustion is often used in combination with acupuncture, but it may also
be performed separately. The main difference between moxibustion and acupuncture
is that the former applies heat instead of mechanical stimulus to the point.
It is indicated chiefly for deficiency syndromes with cold manifestations such
as pain aggravated by cold-Moxa wool, made of dry moxa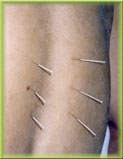 leaves (Artemisia vulgaris) ground into a cotton-like substance, is shaped into
a moxa stick about 2O cm long and 1.4 cm in diameter. An ignited moxa stick
is held about an inch from the patient's skin, warming the point until it reddens
or it is held nearer to the skin and moved up and down so as to apply more heat
to the point. A single treatment of moxibustion usually lasts 10-l5 minutes.
leaves (Artemisia vulgaris) ground into a cotton-like substance, is shaped into
a moxa stick about 2O cm long and 1.4 cm in diameter. An ignited moxa stick
is held about an inch from the patient's skin, warming the point until it reddens
or it is held nearer to the skin and moved up and down so as to apply more heat
to the point. A single treatment of moxibustion usually lasts 10-l5 minutes.
Acupuncture is a non-specific therapy which aims to regulate various body functions. It may be used clinically as the primary treatment or as an adjunct for relieving certain symptoms. In l979 the world Health Organization formulated a list of 43 diseases that can be treated by acupuncture. Recently, however, it has been reported effective for about 250 kinds of diseases. Its special therapeutic effect has been shown to work with diseases refractory to Western treatment: immure diseases, drug addictions, psychogenic diseases and functional disorders